PROJECT RELIEF MEASUREMENTS
INDEX
1. 3D SCANNING
2. REVERSE ENGINEERING: INDUSTRY 4.0
3. SUMMARY ON 3D SCANNER
3D SCANNING
Reproducing a piece you already have to perfection can be a bit tricky. The difficulties increase if the part to be reproduced is a mechanical element; in these cases, high precision is essential, or else an entire machine will function.
Until recently, the process of reproducing one or more parts that were no longer available on the market was no small problem for industrialists; in some cases, the very high cost of this operation (it is the impossibility of reproducing certain types of objects correctly) could steer the company owner toward a radical solution, namely the complete replacement of the machinery to be repaired.
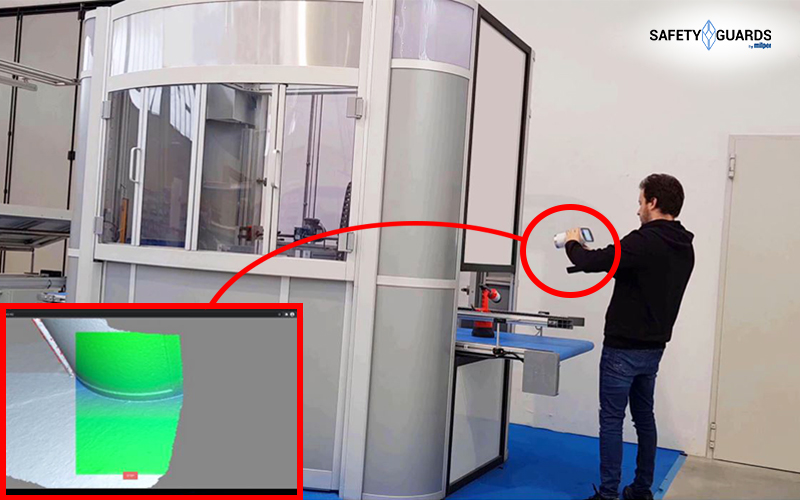
Today, fortunately, technology can help solve this problem, thanks to the 3D scanning. With optical scanning systems, incredibly precise measurements can be made, reproducing any type of object.
The applications of this technology are virtually endless: with the 3D Scanning it is possible to reproduce both small objects and mechanical parts at high precision; in addition, this type of measurement also finds use in the mining sector and more generally in the primary sector, where large mechanical or structural parts, must be replaced with some regularity to ensureefficiency Of the facilities.

REVERSE ENGIGNEERING: INDUSTRY 4.0
True, 3D Scans, as well as methods of measuring and reproducing objects, are true works of Reverse Engineering. That is: the pre-existing object will be thoroughly analyzed, measured in every part, improved where necessary, and finally reproduced.
To date, there are 2 methodologies available: the manual method and 3D Scanning, a rather recent technology. The manual method consists of measuring (with meters, micrometers, protractors, etc.) each part of the part. The measurements will then be used to create digital models, with CAD-type programs; the resulting model will, later, be industrially reproduced.
This methodology has obvious limitations: the measurements made with analog instruments, as well as measurements, more generally, made by a person, introduce the possibility of human errors. In addition, each instrument used to take measurements, has its own sensitivity, this means that the measurements, could be slightly inaccurate, depending on the skill of the operator. In general, manual measurement and design operations, especially on very complex parts, take a lot of time, which results in high costs.
La 3D Scanning reduces variables related to operator skill, instrument sensitivity and possible human error. This type of survey, is carried out using a 3D Scanner. Able to read and measure With greater precision any artifact or mechanical part.
The result returned by the machine, will be used to generate a 3D model on the operator’s PC; later, that “raw” digital model will be used to create a digital solid, ready for the production line. This system is much less time-consuming, compared to manual measurement, and is therefore considerably cheaper; it also features a great precision.
SUMMARY ON 3D SCANNER
As we have seen, the 3D Scanning is a state-of-the-art system capable of offering extremely precise measurement of objects and the creation of digital, production-ready solid models. The 3D Scanning system is carried out thanks to 3D Scanners, equipped with optical readers incredibly accurate, extremely efficient even on the software side.
These machines guarantee excellent results in a very short time, therefore, the system of 3D scanning and modeling, is often cheaper and more accurate, compared to the classic manual method.


